Keep up to date with our innovative initiatives.
Sign up here

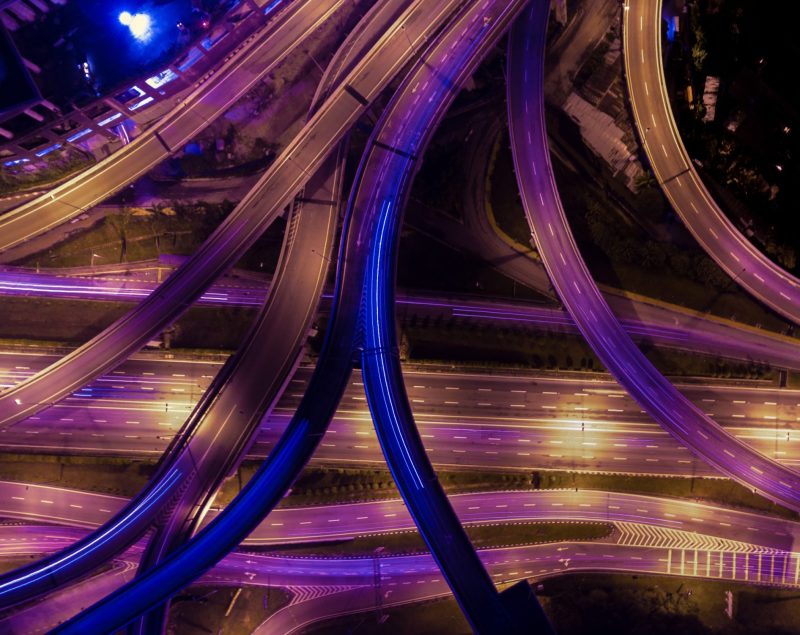
Proactive prevention of traffic accidents through the identification of risk situations and analysis of traffic flows based on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data.


As part of an initiative by the Center of Innovation for Data tech and Artificial Intelligence (CIDAI), the i2CAT Foundation has led the development of a risk and traffic flow detection system on urban and interurban roads based on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data.
The system, created under the framework of the so-called PAI Mobilitat project, has been developed in collaboration with the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), the Centre de Telecomunicacions i Tecnologies de la Informació (CTTI), Eurecat and Microsoft, and it provides intelligent mobility solutions with two main objectives:
The i2CAT Foundation has developed a video processing system based on deep learning algorithms and computer vision to identify all the objects on the road and extract their position, trajectory and speed information.
The centre has also designed a semantic corpus including road information (lanes, traffic directions, traffic lights, etc.) and a series of regulations that describe the different risk situations according to the type of road (urban or interurban). Through this information, i2CAT has also generated semantic maps that, together with the information of the video analysis system, can identify precisely the risks associated with driving.
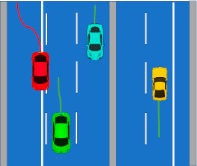
Unauthorised lane changes
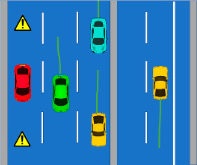
Vehicles stopped on the road
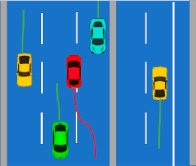
Vehicles driving in the opposite direction
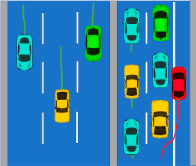
Vehicles driving on the side of the road

Lack of safety distance

Pedestrians crossing unauthorized zones
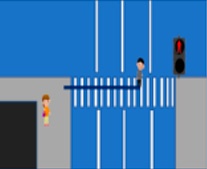
Pedestrian crossing at a red light
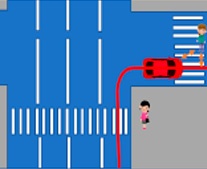
Vehicles that get too close to pedestrians
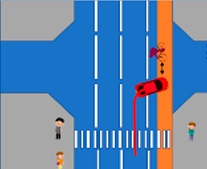
Vehicles that get too close to bikes
The system has allowed the detection and tracking of multiple types of vehicles at different times of the day. Researchers have been able to demonstrate the system’s efficiency thanks to the correct identification of 83,45% of risk situations.
This technological solution allows administrations to implement proactive prevention plans to substantially reduce traffic accidents and deaths on the road.
In turn, it would allow significant improvements in the flow of traffic and the reduction of polluting gases thanks to the minimization of traffic jams and the optimization of waiting time at traffic lights in cities.






