
Keep up to date with our innovative initiatives.
Sign up here
The evolution of data networks towards Software Defined Networks (SDN) provides more flexible and scalable network deployments by defining a decoupled control plane based on well-defined controllers. TSN networks also follow this tendency by defining a fully-centralized control plane architecture with two controllers: the Centralised User Configuration (CUC) and the Centralised Network Configuration (CNC), as depicted in the figure below. The availability of these controllers enables the usage of Machine Learning (ML) algorithms intended to assign network resources to the end users. 6GSMART-EZ proposes a set of ML models based on Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to perform the routing and scheduling of data frames across TSN networks.
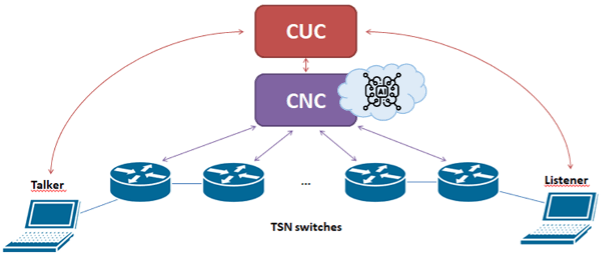
The CNC module is responsible for receiving resource requests from the CUC module (generated by end devices), assigning the requested resources, and configuring the TSN switches according to the resource allocation. The assignment method is based mostly on Integer Linear Programming (ILP) solvers, which provide optimal solutions in non-real time. In 6GSMART-EZ, UPC has developed a set of DRL models that are deployed in the CNC module with the aim of creating the shortest paths between end devices in real-time. We understand that the shortest path in terms of routing is based on traversing the links with the lowest possible delays. Regarding scheduling, we optimized the models so that the buffering time of data frames at intermediate switches is minimized, enabling synchronous communications.
The developed DRL models are based on the Deep Q-Networks algorithm (DQN), and several simulations have been conducted with the aim of testing its behaviour. Two kinds of models have been implemented:
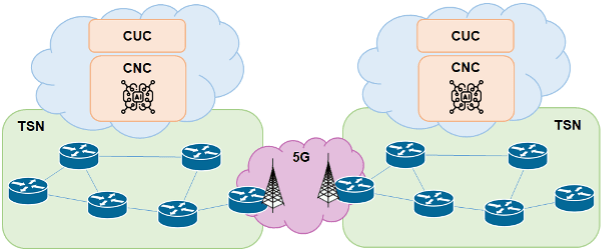
The distributed approach provides the required flexibility and scalability to support the 5G-TSN integration conducted within the 6G-SMART-EZ project. Moreover, the independence between both agents enables the interconnection of several TSN networks managed by different entities since security and privacy are key features of this implementation (e.g. no data related to end-users is shared between entities).
More details and results can be found in the following publication: S. Garcia-Cantón, C. Cervelló-Pastor, D. Rincón and S. Sallent, “Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint Scheduling and Routing for Time-Sensitive Networks”, in 2024 24th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 2024, pp. 1-4
Author: Sergi Garcia-Cantón, Researcher at the Design and Evaluation of Broadband Networks and Services (BAMPLA) research group of the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)